By Nancy Lapid
The following is a summary of some recent studies on COVID-19. They include research that warrants further study to corroborate the findings and that has yet to be certified by peer review.
COVID-19 and flu make for a dangerous combo
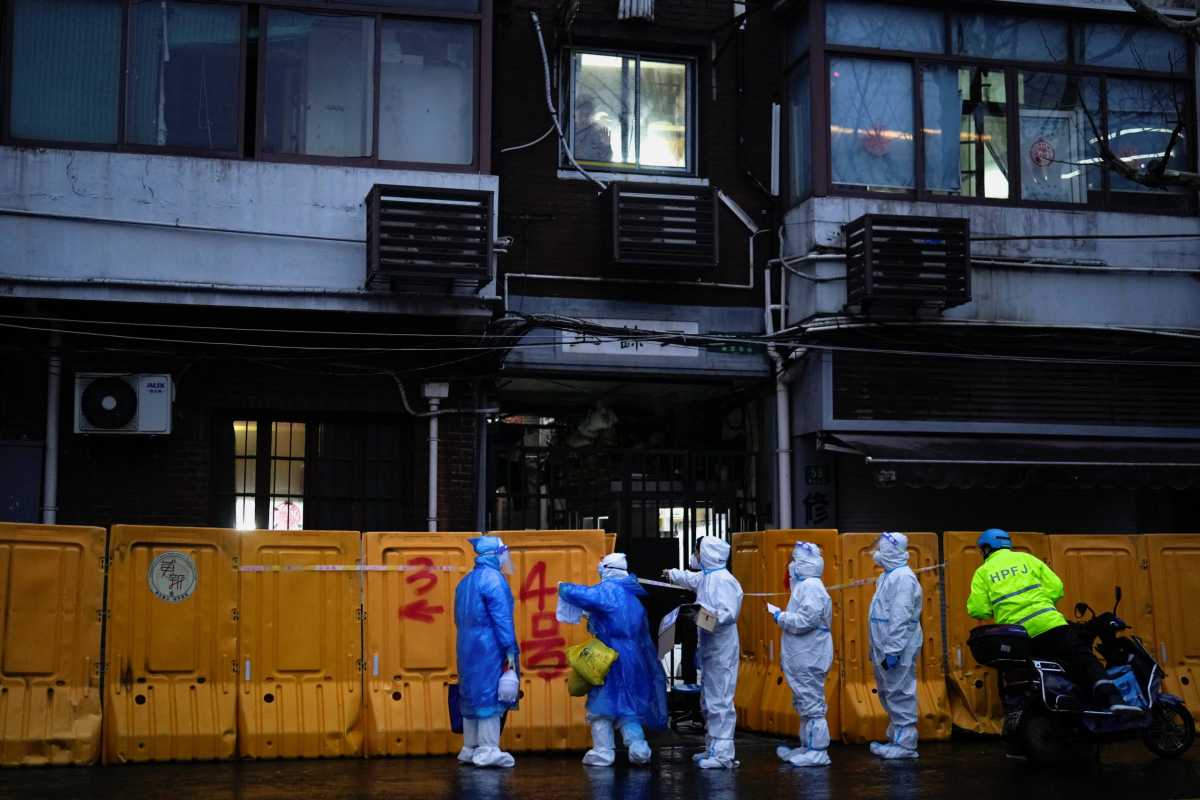
Having COVID-19 and influenza at the same time puts hospitalized adults at much greater risk of critical illness and death compared to having COVID-19 without the flu, researchers reported on Friday in The Lancet.
Patients with SARS-CoV-2/influenza co-infections were more than four times as likely to require machines to help them breath and 2.4 times as likely to die compared to patients who only had COVID-19, according to a study of nearly 7,000 hospitalized patients with COVID-19, including 227 who also had the flu. Dr. Kenneth Baillie of the University of Edinburgh, who led the study, said the combination of the two viruses is particularly dangerous.
“We expect that COVID-19 will circulate with flu, increasing the chance of co-infections. That is why we should change our testing strategy for COVID-19 patients in hospital and test for flu much more widely,” Baillie said in a statement.
“The vaccines that protect against COVID-19 and flu are different,” added Dr. Peter Openshaw of Imperial College London, “and people need both.”
HIV drugs may curb COVID-19 risk
Certain drugs used to treat HIV may have a role in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infections, according to preliminary data that may help explain why people living with the condition have not appeared to be at higher risk for serious COVID-19 despite being generally more vulnerable to infections.
Doctors in France studied more than 500 people with HIV, a third of whom were receiving long-term treatment with protease inhibitor drugs as part of their antiviral therapy. Over the course of a year, SARS-CoV-2 infections were diagnosed in 12% of participants taking protease inhibitors and 22% of those not receiving these drugs. Four patients in the non-protease-inhibitor group were admitted to hospital with COVID-19. After accounting for other risk factors, individuals taking protease inhibitors were 70% less likely to become infected with SARS-CoV-2 than patients who were not taking these drugs, according to data scheduled for presentation at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
Some new treatments for COVID-19 use protease inhibitors, which block the virus from multiplying. “Protease inhibitor drugs have long history of use, a good safety profile, and are generally well tolerated,” Dr. Steve Nguala from the Intercommunal Hospital Center of Villeneuve-Saint-Georges, said in a statement. They have the potential “to prevent the spread of infections and mutation of future variants,” he said, adding that larger studies are needed to confirm the findings.
Reuters