By Clodagh Kilcoyne
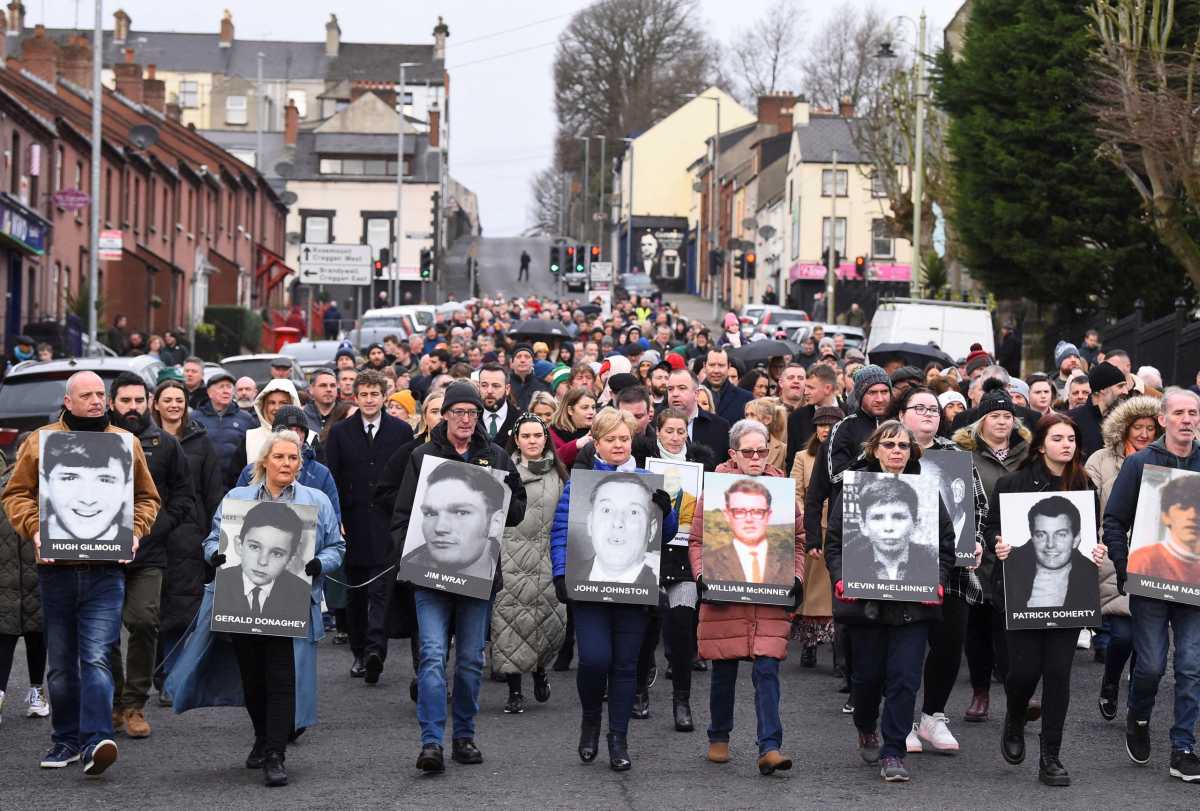
LONDONDERRY – Ireland on Sunday called on Britain to ensure justice for the families of 13 peaceful protesters shot dead by its soldiers on “Bloody Sunday” in 1972 as thousands marked the 50th anniversary of one of the defining days of the Northern Ireland conflict.
The British government in 2010 apologized for the “unjustified and unjustifiable” killings of 13 Catholic civil rights protesters by British soldiers in the Northern Irish city of Londonderry on Jan. 30, 1972 — and of a 14th who died later of his wounds.
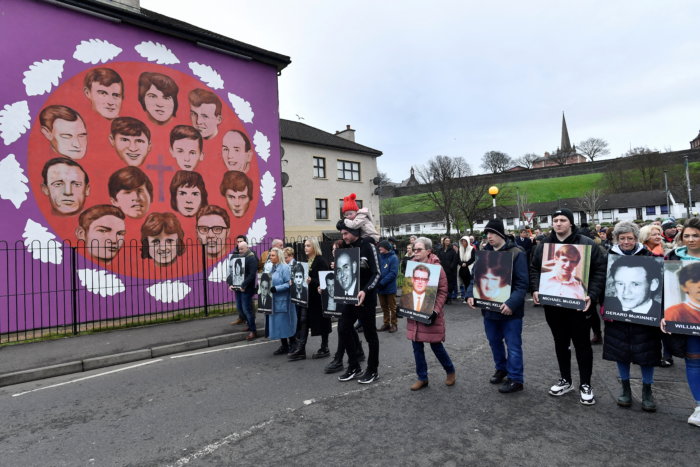

None of those responsible for the shootings has been convicted and last July British prosecutors said the only British soldier charged with murder will not face trial — a decision that is being challenged by relatives.
“There should be a route to justice,” Irish Foreign Minister Simon Coveney told state broadcaster RTE after laying a wreath and meeting with relatives of the victims.
“As somebody said, our children were buried 50 years ago but we still haven’t laid them to rest … because we don’t have justice,” he said.
Coveney reiterated the Irish government’s opposition to a proposal by British Prime Minister Boris Johnson’s government to halt all prosecutions of soldiers and militants to try to draw a line under the conflict — a move that angered relatives and has been rejected by all the main local political parties.
“We absolutely cannot and will not support that approach,” he said.
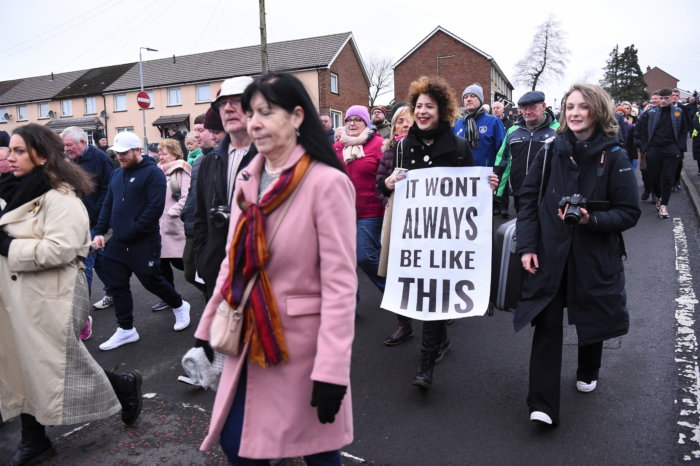

Relatives holding white roses and photographs of those killed led thousands of people in retracing route of the 1972 march in Sunday’s memorial events.
Irish Prime Minister Micheal Martin looked on as the names of all the Bloody Sunday victims were read out.
“The full process of the courts and of justice should be deployed,” Martin told journalists after the ceremony.
No-one from the British government attended the events and senior loyalist Northern Irish politicians also stayed away.
Johnson in a Twitter post on Saturday described Bloody Sunday as “one of the darkest days of the Troubles” and said Britain must learn from the past.
A spokesperson for the British government said it was “absolutely committed to addressing legacy issues comprehensively and fairly.”
“This will include measures that focus on information recovery, so that families can know what happened to their loved ones, and which promote reconciliation, so all communities in Northern Ireland can move forward,” the spokesperson said.
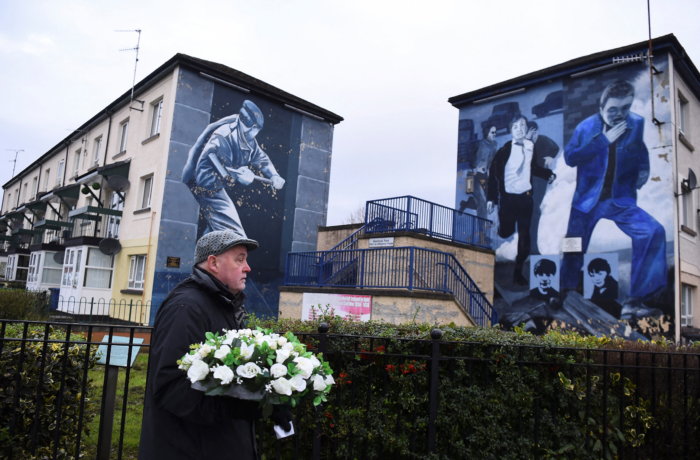

More than 3,000 people were killed before the 1998 peace process largely ended years of conflict between Irish nationalist militants seeking unification with the Republic of Ireland and the British Army and loyalists determined to keep the region of Northern Ireland under British rule.